While the pandemic was a wave of economic disruptions for many industries, it has blown some exemplary achievements to the Indian pharmaceutical industry. The pharmaceutical industry in India is currently valued at $41.7 bn. However, the pharmaceutical industry in India is expected to reach $65 bn by 2024 and $120 bn by 2030. Moreover, in August 2021, the Indian pharmaceutical market increased at 17.7% annually, up by 13.7% in July 2020. According to India Ratings and Research, the Indian pharmaceutical market revenue will be over 12% Y-o-Y in FY22.
India ranks 3rd worldwide for production by volume and 14th by value. In addition, India has the highest number of US-FDA compliant Pharma plants outside of the USA. It is home to more than 3,000 pharma companies with a strong network of over 10,500 manufacturing facilities.
Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Goa are the major pharmaceutical manufacturing clusters in the country. The bulk drug clusters are located primarily in Ahmedabad, Vadodara, Mumbai, Aurangabad, Pune, Hyderabad, Chennai, Mysore, Bangalore, and Visakhapatnam (Vizag).
The pharmaceutical hubs offer investment opportunities to produce API or bulk drugs, vaccines, nutraceuticals, food and drug testing, clinical research, research and development, and contract research/manufacturing. Multinational pharmaceutical corporations outsource these various activities and help the sector’s growth. As a result, the Indian Pharmaceutical companies have a promising future. We will discuss prominent aspects of the industry and outline the growing Indian pharmaceutical industry.
India is the largest provider of generic drugs in the global pharmaceutical industry
- India is the largest provider of generic drugs globally. India’s generic drug producers hold a strong position in the global supply chain and play an integral role in developing the pharmaceutical industry. The pharma industry in India produces around 20% to 24% of the global generic drugs.
- Indian pharmaceutical sector supplies 40% of generic demand in the US and 25% of all medicines in the UK. The pharmaceutical industry in India offers 60,000 generic brands across 60 therapeutic categories.
- Indian pharmaceutical companies supply over 80 percent of the anti-retroviral drugs used globally to combat AIDS (Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome). Furthermore, six domestic firms – Aurobindo, Cipla, Desano, Emcure, Hetero Labs, and Laurus Labs have a sublicense with the UN-backed Medicines Patent Pool to manufacture anti-AIDS medicine TenofovirAlafenamide (TAF) for 112 developing countries.
Increased profits in the pharmaceutical industry from exports of the pharmaceutical products
The country’s pharmaceutical sector contributes 6.6% to the total merchandise exports. India exports around 40% of its pharmaceutical products to more than 200 countries globally. Of these, 55% of the total exports constitute formulations, and the other 45% comprises bulk drugs.
According to the Pharmaceutical Export Council of India (Pharmexil), 55 percent of Indian exports are sent to highly regulated markets. The United States is the most lucrative generics market for India’s pharma industry. It is valued at around $60 billion and accounts for about 25 percent of India’s total shipment. India’s other important export destinations include the United Kingdom, South Africa, Russia, and Nigeria.
The significant growth rate in exports of pharmaceuticals over the past few years can be seen below:
- In 2017-18, India exported pharmaceutical products worth US$17.27 billion.
- In 2018-19, India’s pharmaceuticals exports were worth US$19.3 billion, showing a growth of 10.72 percent year on year.
- In 2019-20, exports grew to US$20.5 billion.
- By 2020-21, the industry estimates exports to grow to US$25 billion.
- This year, India’s pharma exports in the first six months amounted to US$11.38 billion, which was nearly 15 percent higher than in the same period last year.

Foreign investments in due to the low cost of productions
With the large concentration of multinational pharmaceutical companies in India, it becomes easier to attract foreign direct investments. Therefore, the pharma industry in India is one of the essential foreign direct investment encouraging sectors. India’s current foreign direct investment (FDI) policy allows acceptance of 100 percent FDI under the automatic route in greenfield pharmaceutical projects. It also allows 74 percent FDI acceptance under the automatic route in brownfield projects – upwards of which can still be allowed through the government approval.
India is also emerging as a preferred destination for contract manufacturing organizations. Indian contract manufacturing companies are gaining popularity because India has a low cost of production, low R&D costs, an innovative scientific workforce, and a large number of national laboratories that have the potential to steer the industry ahead. As per industry analysts, the manufacturing cost in India is approximately 33 percent lower than that of the US. Thus more companies are directing their manufacturing outsourcing in India and focusing more on their new drug discoveries.
Hold of the API industry
The Indian Pharmaceutical Industry is one of the biggest producers of active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) in the international arena. India has more than 262 API manufacturing USFDA approved plants. India is 3rd most prominent market for APIs globally and has an 8% share in the Global API Industry. API pharma companies in India produce 500+ different APIs, and it contributes 57% of APIs to prequalified list of the WHO.
Supply of vaccines during and before the pandemic
India is the largest producer of vaccines worldwide, accounting for around 60% of the total vaccines in 2021. In addition, India’s pharmaceutical industry is among the leading global producers of cost-effective generic medicines and vaccines. It supplies 20 percent of the global demand by volume and 62 percent of the global demand for vaccines. Therefore, it is expected to play a vital role in meeting the global demand for COVID-19 vaccines, especially for low and middle-income countries.
As of May 2021, India supplied a total of 586.4 lakh COVID-19 vaccines, comprising grants (81.3 lakh), commercial exports (339.7 lakh), and exports under the COVAX platform (165.5 lakh) to 71 countries.
The above-discussed facts prove that the pharmaceutical sector is highly profitable for the Indian economy and a global benchmark.
For more such insights, stay tuned to our website https://newedgeoverseas.com/.
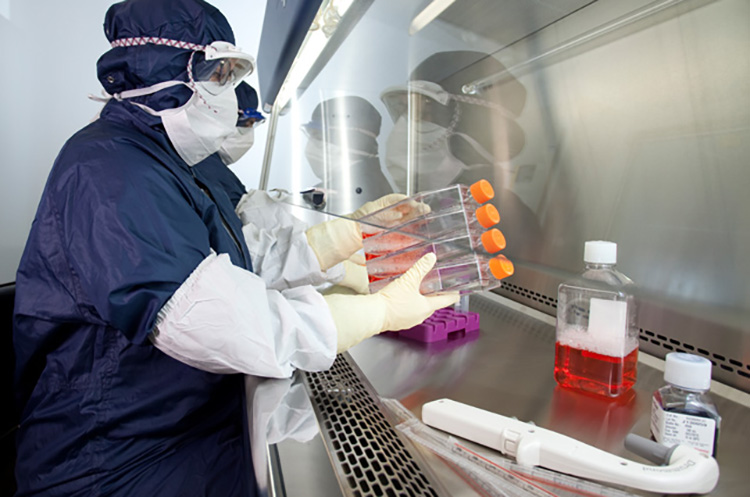







 The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is responsible for protecting public health by assuring the safety, efficacy, and security of human and veterinary drugs, biological products, medical devices, the nation’s food supply, cosmetics, and products. FDA is also responsible for advancing public health by helping to speed innovations that make medicines safer, more effective, and more affordable.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is responsible for protecting public health by assuring the safety, efficacy, and security of human and veterinary drugs, biological products, medical devices, the nation’s food supply, cosmetics, and products. FDA is also responsible for advancing public health by helping to speed innovations that make medicines safer, more effective, and more affordable. The Medicines & Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) is the government agency responsible for ensuring the proper use of medicine and medical devices. The MHRA is an executive agency of the Department of Health.
The Medicines & Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) is the government agency responsible for ensuring the proper use of medicine and medical devices. The MHRA is an executive agency of the Department of Health. The Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency (Anvisa) is an autarchy linked to the Ministry of Health, part of the Brazilian National Health System (SUS) as the coordinator of the Brazilian Health Regulatory System (SNVS), present throughout the national territory.
The Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency (Anvisa) is an autarchy linked to the Ministry of Health, part of the Brazilian National Health System (SUS) as the coordinator of the Brazilian Health Regulatory System (SNVS), present throughout the national territory. The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) is the regulatory authority for the Australian pharmaceutical industry. The TGA oversees and regulates numerous therapeutic goods, including prescription medicines, vaccines, and medical devices. The site contains information specific to consumers, health professionals, and industry manufacturers. It also lists recent pharmaceutical recalls and alerts.
The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) is the regulatory authority for the Australian pharmaceutical industry. The TGA oversees and regulates numerous therapeutic goods, including prescription medicines, vaccines, and medical devices. The site contains information specific to consumers, health professionals, and industry manufacturers. It also lists recent pharmaceutical recalls and alerts. The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization in India sets standards and regulatory measures for medications. Further, the organization guides on health issues and medicines. They also regulate the standards of imported drugs and clinical research in India. Various regulatory documents and forms are available to download for free in PDF from the website.
The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization in India sets standards and regulatory measures for medications. Further, the organization guides on health issues and medicines. They also regulate the standards of imported drugs and clinical research in India. Various regulatory documents and forms are available to download for free in PDF from the website. WHO (World Health Organization) is the United Nations specialized agency for health. It is responsible for providing leadership on global health matters shaping the health research agenda, setting norms and standards, articulating evidence-based policy options, providing technical support to countries, and monitoring and assessing health trends. In addition, it is the United Nations agency that connects nations, partners, and people to promote health, keep the world safe, and serve the vulnerable. So everyone can attain the highest level of health.
WHO (World Health Organization) is the United Nations specialized agency for health. It is responsible for providing leadership on global health matters shaping the health research agenda, setting norms and standards, articulating evidence-based policy options, providing technical support to countries, and monitoring and assessing health trends. In addition, it is the United Nations agency that connects nations, partners, and people to promote health, keep the world safe, and serve the vulnerable. So everyone can attain the highest level of health. The International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) is unique in bringing together the regulatory authorities and pharmaceutical industry to discuss pharma-related scientific and technical aspects and develop guidelines. Since its inception in 1990, ICH has gradually evolved to respond to increasingly global developments in the pharmaceutical sector.
The International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) is unique in bringing together the regulatory authorities and pharmaceutical industry to discuss pharma-related scientific and technical aspects and develop guidelines. Since its inception in 1990, ICH has gradually evolved to respond to increasingly global developments in the pharmaceutical sector. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) protects and promotes public health by evaluating medicines. The EMA provides recommendations on the quality and safety of medicines. In addition, they apply evaluation procedures to help bring new medicines to the European Union.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) protects and promotes public health by evaluating medicines. The EMA provides recommendations on the quality and safety of medicines. In addition, they apply evaluation procedures to help bring new medicines to the European Union. Health Canada is responsible for helping Canadians maintain and improve their health. It ensures that high-quality health services are accessible and works to reduce health risks. They focus on product safety, environmental and workplace health, food and nutrition, health and science research, drugs and health products, etc.
Health Canada is responsible for helping Canadians maintain and improve their health. It ensures that high-quality health services are accessible and works to reduce health risks. They focus on product safety, environmental and workplace health, food and nutrition, health and science research, drugs and health products, etc. In 2008, the Ministry of Health established the Egyptian Drug Authority (EDA) to have an independent regulatory body responsible for all pharmaceutical-related activities. It is similar to the function of India’s FDA in the United States. This establishment was seen as a landmark restructuring in the Egyptian pharmaceutical industry. There had yet to be an independent and organized body to manage pharmaceutical regulatory affairs beforehand.
In 2008, the Ministry of Health established the Egyptian Drug Authority (EDA) to have an independent regulatory body responsible for all pharmaceutical-related activities. It is similar to the function of India’s FDA in the United States. This establishment was seen as a landmark restructuring in the Egyptian pharmaceutical industry. There had yet to be an independent and organized body to manage pharmaceutical regulatory affairs beforehand.